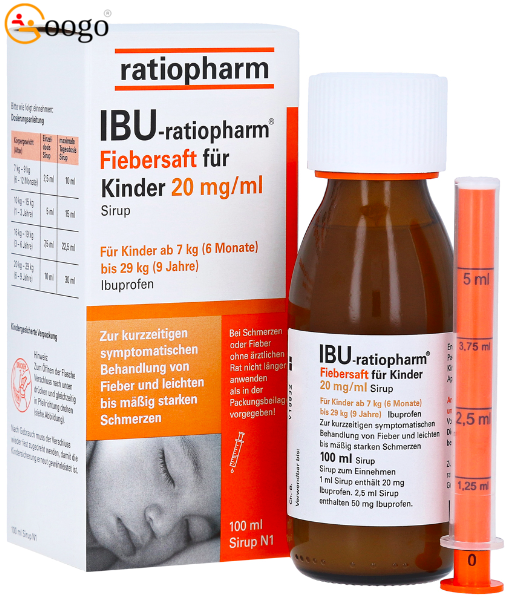
For pain and fever for children from 7 kg
The fever juice with the active ingredient ibuprofen is an analgesic and antipyretic drug for short-term symptomatic treatment of mild to moderate pain and fever in children between 7 kg (approx. 6 months) and 29 kg (approx. 9 years). With a delicious strawberry cream taste.
Lactose free. Contains sucrose and glucose.
- Mild to moderate pain, such as:
- headache
- toothache
- fever
The total dose should not be exceeded without consulting a doctor or pharmacist.
Type of application?
Take the medicine. You can also dilute the medicine with water or tea. Shake well before use.
Duration of use?
You should not use the medicine for more than 3 days without medical advice.
overdose?
An overdose can cause headaches, dizziness, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, drop in blood pressure, drowsiness and breathing disorders. If you suspect an overdose, contact a doctor immediately.
Forgot to take?
Continue taking it as normal (i.e. not double the amount) at the next prescribed time.
In general, pay attention to a conscientious dosage, especially for infants, small children and the elderly. If in doubt, ask your doctor or pharmacist about any effects or precautions.
A dosage prescribed by the doctor may deviate from the information on the package leaflet. Therefore, since the doctor adjusts them individually, you should use the medicine according to his instructions.
active ingredients
- 100 mg ibuprofen
excipients
- xanthan gum
- Sodium saccharine
- 450 mg glucose
- Macrogol 900000
- Sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment
- Hydrochloric acid for pH adjustment
- Strawberry Cream Flavor
- water, purified
- sodium chloride
- sodium bicarbonate
- 1000 mg sucrose
- Citric acid monohydrate
- cornstarch
- 15 mg propylene glycol
- Polysorbate 80
- potassium sorbate
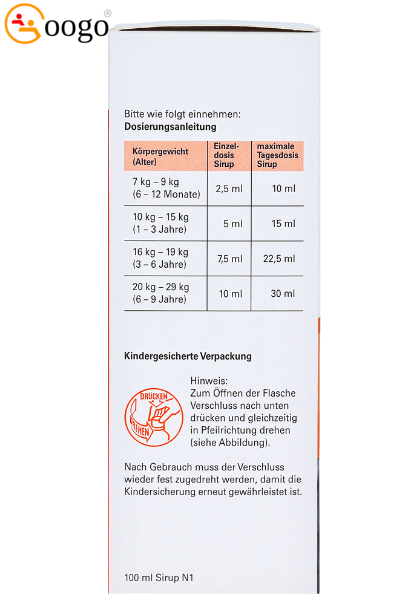
Dosage:
| General dosage recommendation: | |||
| group of people | single dose | total dose | time |
| Babies from 6-12 months (weighing 7-9 kg) |
2.5ml | 1-4 times a day (max. 10ml per day) |
6 hours apart, regardless of the meal |
| Small children from 1-3 years (with 10-15kg body weight) |
5ml | 1-3 times a day (max. 15ml per day) |
6 hours apart, regardless of the meal |
| Children from 3-6 years (with 16-19kg body weight) |
7.5ml | 1-3 times a day (max. 22.5ml per day) |
6 hours apart, regardless of the meal |
| Children from 6-9 years (with 20-29kg body weight) |
10ml | 1-3 times a day (max. 30ml per day) |
6 hours apart, regardless of the meal |
- Always use this medicine exactly as directed or as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- The recommended dose is:
- 7 kg - 9 kg (infants 6 - 12 months)
- Single dose: 2.5 ml (equivalent to 50 mg ibuprofen)
- Maximum daily dose: 10 ml (equivalent to 200 mg ibuprofen)
- 10 kg - 15 kg (children 1 - 3 years)
- Single dose: 5 ml (equivalent to 100 mg ibuprofen)
- Maximum daily dose: 15 ml (equivalent to 300 mg ibuprofen)
- 16 kg - 19 kg (children 3 - 6 years)
- Single dose: 7.5 ml (equivalent to 150 mg ibuprofen)
- Maximum daily dose: 22.5 ml (equivalent to 450 mg ibuprofen)
- 20 kg - 29 kg (children 6 - 9 years)
- Single dose: 10 ml (equivalent to 200 mg ibuprofen)
- Maximum daily dose: 30 ml (equivalent to 600 mg ibuprofen)
- 7 kg - 9 kg (infants 6 - 12 months)
- In children, the dose of ibuprofen depends on body weight (bw) or age, usually with 7 to 10 mg/kg bw as a single dose, up to a maximum of 30 mg/kg bw as a total daily dose.
- Use in children under 7 kg (6 months) is not recommended.
- Please talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you have the impression that the effect of this medicine is too strong or too weak.
- duration of use
- For short-term use only
- If children are required to take this medicine for more than 3 days or if symptoms worsen, medical advice should be sought.
- If you use more ibuprofen than you should
- If you have given your child more ibuprofen than you should, or if children have accidentally taken the medicine, always contact your nearest doctor or hospital for an assessment of the risk and advice on further treatment.
- Symptoms can include nausea, stomach pain, vomiting (possibly with blood), headache, ringing in the ears, confusion, and eye tremors. At high doses, drowsiness, chest pain, palpitations, fainting, convulsions (especially in children), weakness and dizziness, blood in the urine, feeling cold and breathing problems have been reported. Severe intoxication can also cause visual disturbances and (rarely) hypotension and acute renal failure.
- If you forget to use ibuprofen
- Do not apply a double dose to make up for a forgotten application.
- If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- To take.
- For precise dosing, the package includes an application aid printed with a measuring scale for preparations to be taken.
- To apply, please proceed as follows:
- Shake the bottle before use!
- Open the bottle by pressing the cap down while turning it in the direction of the arrow.
- After use, screw the lid on tightly to snap the child-resistant closure back into place.
- Patients with sensitive stomachs are advised to take ibuprofen with a meal.
- See package leaflet for more information.
What speaks against an application?
Always:
- Hypersensitivity to the ingredients
- Hematopoietic
disorders - Ulcers in the digestive tract, also in the past
- Bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, also in the past
- Active bleeding, such as:
- Cerebral hemorrhage
- Impaired liver function
- Impaired kidney function
- Heart failure
- Severe dehydration
Under certain circumstances - talk to your doctor or pharmacist about:
- gastrointestinal complaints
- inflammatory bowel diseases, also in the past, such as:
- Crohn's disease
- ulcerative colitis
- high blood pressure
- Collagenosis (changes in the connective tissue area), such as:
- Lupus erythematosus
- Mixed collagenosis (inflammatory rheumatic collagenosis)
- Porphyria (metabolic disease)
- Major surgery that has taken place shortly before
- Chickenpox
Which age group should be considered?
- Babies under 6 months: The medicine must not be used.
- Elderly patients over 65 years of age: The treatment should be coordinated with your doctor and carefully monitored, for example by means of close checks. The desired effects and undesired side effects of the drug can be stronger or weaker in this group.
What about pregnancy and lactation?
- Pregnancy: consult your doctor. Various considerations play a role in whether and how the drug can be used during pregnancy.
- Breast-feeding: consult your doctor or pharmacist. He will examine your particular starting position and advise you accordingly as to whether and how you can continue breastfeeding.
If you have been prescribed the drug despite a contraindication, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. The therapeutic benefit can be higher than the risk that the use entails in the event of a contraindication.
What adverse effects may occur?
- Gastrointestinal complaints, such as:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Heartburn
- Flatulence
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Abdominal pain
- Bleeding in the gastrointestinal area
- Tarry stools, please consult a doctor immediately if they occur - Inflammation of the
gastric mucosa
- Ulcers in the digestive tract, which can be very can also rarely break through
- headache
- dizziness
- tiredness
- insomnia
- irritability
- agitation
- hypersensitivity reactions of the skin, such as:
- skin rash
- itching
- attacks of shortness of breath
- Visual disturbances, please consult a doctor immediately if they occur . If you notice any
changes in your condition or changes during treatment, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
For the information at this point, side effects are primarily taken into account that occur in at least one in 1,000 patients treated.
Storage
The medicinal product may be used for a maximum of 1 year after opening/preparation!
The medicinal product must be stored at room temperature after opening/preparation
What should you consider?
- The ability to react can also be impaired when used as intended, especially in higher doses or in combination with alcohol. Be particularly careful when driving or operating machines (including household ones) that could injure you.
- In case of pain or fever, do not use longer than specified in the leaflet without medical advice!
- With long-term use of painkillers, headaches caused by the painkiller can occur. Talk to your doctor to prevent your headache from becoming chronic.
- The habitual use of painkillers can lead to permanent kidney damage. If several painkillers are combined, or if one painkiller contains several active ingredients, the risk increases.
- Caution: Patients with nasal polyps, chronic respiratory infections, asthma or people who are prone to allergic reactions such as hay fever: the drug can trigger an asthma attack or a severe allergic skin reaction. Therefor consult your doctor before usage.
- Be careful if you are allergic to painkillers!
- Be careful if you are allergic to the sweetener saccharin (E number E 954)!
- Be careful if you have an intolerance to glucose. If you have to follow a diabetic diet, you should consider the sugar content.
- Beware of intolerance to sucrose. If you have to follow a diabetic diet, you should consider the sugar content.
- There may be medicines with which interactions occur. You should therefore generally tell your doctor or pharmacist about any other medicine you are already using before starting treatment with a new medicine. This also applies to medicines that you buy yourself, use only occasionally or have been using for some time.
- Alcohol consumption should be avoided during long- term treatmentbe avoided as much as possible. Occasional alcohol consumption in small amounts is allowed, but not with the drug.
How does the ingredient of the medicine work?
The active ingredient belongs to a group of substances that act against pain and inflammation and can reduce fever. All three effects are primarily based on the inhibition of an endogenous substance called prostaglandin. This substance must be present as a messenger substance so that pain can be felt, inflammatory reactions can be started or the body temperature can be raised.
What is included in medicines?
| The amounts given are based on 5 ml of syrup. |
|
| Active ingredient Ibuprofen | 100mg |
| excipient sucrose | 1000mg |
| excipient glucose | 450mg |
| Excipient xanthan gum | + |
| Excipient polysorbate 80 | + |
| Citric acid monohydrate excipient | + |
| Excipient potassium sorbate | + |
| Excipient sodium saccharin | + |
| Excipient strawberry cream flavor | + |
| Excipient propylene glycol | 15mg |
| Excipient corn starch | + |
| Excipient sodium chloride | + |
| Additive table salt | + |
| Excipient macrogol 900000 | + |
| Excipient sodium bicarbonate | + |
| excipient baking soda | + |
| Excipient sodium bicarbonate | + |
| Auxiliary hydrochloric acid for pH adjustment | + |
| Auxiliary sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment | + |
| Excipient water, purified | + |
side effects
- Like all medicines, this can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them.
- The following list of undesirable effects includes all known side effects from treatment with ibuprofen, including those from high-dose long-term therapy in rheumatism patients. The frequency information, which goes beyond very rare reports, relates to short-term use up to daily doses of a maximum of 1200 mg ibuprofen for oral dosage forms and 1800 mg for suppositories.
- With the following side effects, it must be taken into account that they are predominantly dose-dependent and vary between individuals (inter-individually).
- The most frequently observed side effects concern the gastrointestinal tract.
- Ulcers in the stomach and duodenum (peptic ulcers), perforation or bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes fatal, can occur, particularly in elderly patients (see patient information category). Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence, constipation, indigestion, abdominal pain, tarry stools, vomiting blood, ulcerative stomatitis (inflammation of the lining of the mouth with ulceration), aggravation of colitis and Crohn's disease (see patient information category) have been reported after use. Inflammation of the lining of the stomach (gastritis) has been observed less frequently. Medicines like ibuprofen may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack ("myocardial infarction") or stroke.
- If you are affected by any of the following side effects, stop taking the preparation and see your doctor as soon as possible:
- rash and itching
- asthma attack
- Severe hypersensitivity reactions, e.g. B. with swelling of the face, tongue and larynx, narrowing of the airways, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat and drop in blood pressure, which can lead to life-threatening shock.
- Blood disorders: The first signs of this can be fever, sore throat, superficial sores in the mouth, flu-like symptoms, severe exhaustion, nosebleeds and bleeding from the skin. In this case, you should refrain from any self-medication with medicines for pain or fever.
- Exacerbation of inflammation associated with infections (if signs of infection appear or get worse while using ibuprofen).
- visual disturbances
- Relatively severe pain in the upper abdomen, vomiting blood, blood in the stool or black discoloration of the stool.
- Decreased urination and accumulation of fluid in the body (oedema).
- Other possible side effects:
- Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Gastrointestinal complaints such as heartburn, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, diarrhea, constipation and slight loss of blood in the digestive tract, which in exceptional cases can lead to anemia.
- Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Headache, dizziness, insomnia, agitation, irritability or tiredness.
- Hypersensitivity reactions with skin rash and itching or asthma attack (possibly also with drop in blood pressure).
- visual disturbances
- Stomach or intestinal ulcers, possibly with bleeding and perforation.
- Inflammation of the mouth with ulceration (ulcerative stomatitis), worsening of colitis or Crohn's disease, inflammation of the stomach.
- Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Damage to kidney tissue (papillary necrosis), especially with long-term use.
- Increased levels of uric acid in the blood.
- Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- Decreased urine output and accumulation of fluid in the body (oedema), especially in patients with high blood pressure or impaired kidney function. These signs can indicate
kidney disease, sometimes kidney failure. - Nephrotic syndrome (accumulation of fluid in the body [oedema] and excessive protein excretion in the urine), inflammatory kidney disease (interstitial nephritis) which may be accompanied by acute renal dysfunction.
- Hepatic dysfunction, liver damage (especially with long-term therapy), liver failure, hepatitis.
- Hematopoietic disorders (anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis).
- Severe skin reactions such as B. Skin rash with reddening and blistering (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis/Lyell's syndrome), hair loss (alopecia).
- In exceptional cases, severe skin infections and soft tissue complications can occur during chickenpox infection.
- Signs of non-infectious meningitis (aseptic meningitis) such as B. severe headache, nausea, vomiting, fever, stiff neck or impaired consciousness. Patients who have previously had certain immune system disorders
(systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed collagen disease) appear to be at increased risk. - Worsening of infection-related inflammation (e.g. necrotizing fasciitis) has been observed with concomitant use of certain anti-inflammatory drugs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs, of which the drug is a part). - Severe hypersensitivity reactions
- Psychotic reactions, depression.
- Uncomfortably noticeable heartbeat, cardiac insufficiency, heart attack.
- High blood pressure
- Inflammation of the esophagus (oesophagitis), inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), formation of membranous narrowings in the intestine.
- Decreased urine output and accumulation of fluid in the body (oedema), especially in patients with high blood pressure or impaired kidney function. These signs can indicate
- Not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- A severe skin reaction known as DRESS syndrome can occur. Symptoms of DRESS include a rash, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and an increase in eosinophils (a type of white blood cell).
- At the start of treatment a red, scaly, widespread rash with bumps under the skin and blisters accompanied by fever, primarily on the skin folds,
trunk and upper extremities (acute generalized pustular rash). Discontinue use of ibuprofen if you develop these symptoms and seek medical attention immediately (see Contraindications category).
- Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This also applies to side effects that are not specified.
interactions
- Use together with other medicines
- Tell your doctor or pharmacist if your child is taking/using, has recently taken/used or might take/use any other medicines.
- Ibuprofen may affect or be affected by other medicines. For example:
- Medicines that have an anticoagulant effect (i.e. thin the blood/prevent clotting, e.g. acetylsalicylic acid, warfarin, ticlopidine)
- Medicines that lower high blood pressure (ACE inhibitors such as captopril, beta-blockers such as medicines containing atenolol, angiotensin II receptor antagonists such as losartan)
- Some other medicines can also affect or be affected by ibuprofen treatment. You should therefore always seek the advice of your doctor or pharmacist before using ibuprofen with any other medicine.
- Enhanced effect with possibly increased risk of side effects:
- digoxin (medicine to treat heart failure and irregular heartbeat), phenytoin (medicine to treat epilepsy or neuropathic pain), lithium (medicine to treat certain psychiatric disorders):
- Blood levels of these active substances may be increased. If used correctly (maximum 3 days), a blood level check is usually not necessary.
- Anticoagulants (e.g. warfarin): Your blood should be checked for clotting.
- Methotrexate (medicine used to treat cancer and certain rheumatic diseases): Do not administer the drug within 24 hours before or after taking methotrexate. This can lead to increased levels of methotrexate and an increase in its side effects.
- Acetylsalicylic acid and other anti-inflammatory painkillers (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) and glucocorticoids (medicines containing cortisone or cortisone-like substances):
- There is an increased risk of ulcers and bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Platelet aggregation inhibitors and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (medicines used to treat depression):
- There is an increased risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
- digoxin (medicine to treat heart failure and irregular heartbeat), phenytoin (medicine to treat epilepsy or neuropathic pain), lithium (medicine to treat certain psychiatric disorders):
- Weakened effect:
- Water tablets (diuretics) and medicines that lower blood pressure (antihypertensives). There may also be an increased risk for the kidneys.
- ACE inhibitors (medicines used to treat heart failure and high blood pressure). In addition, the risk of developing renal dysfunction is increased.
- Acetylsalicylic acid: If taken at the same time as ibuprofen, the anticoagulant (antithrombotic) effect of low-dose acetylsalicylic acid may be impaired.
- Other possible interactions:
- Zidovudine (medicine used to treat HIV/AIDS): The risk of bleeding into joints (haemarthrosis) and bruising is increased in HIV-positive patients with haemophilia.
- Ciclosporin (medicine to suppress the immune response): There is evidence that kidney damage can occur.
- Tacrolimus: Kidney damage or overdose can occur if the two drugs are given at the same time.
- Potassium-sparing water pills (certain diuretics):
- Simultaneous use can lead to an increase in potassium levels.
- Sulphonylureas (medicines used to treat diabetes): Although interactions between ibuprofen and sulphonylureas, unlike other NSAIDs, have not been described to date, monitoring of blood sugar levels is recommended as a precautionary measure when used concomitantly.
- Probenecid and sulfinpyrazone (medicines used to treat gout): These medicines can delay the elimination of ibuprofen.
- Quinolone antibiotics: There may be an increased risk of seizures.
- Voriconazole and fluconazole (antifungal drugs) may increase ibuprofen exposure.
- Use together with alcohol
- Alcohol consumption should be avoided during treatment with ibuprofen.
Contraindications
- The medicine must not be used
- if your child is allergic to ibuprofen or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- if your child has ever had a reaction to acetylsalicylic acid or any other medicine for pain and inflammation (NSAIDs) with bronchospasm, asthma attacks, swelling of the nasal mucosa, angioedema or skin rash.
- in unexplained blood disorders.
- if you have or have had a history of recurrent stomach/duodenal ulcers (peptic ulcers) or gastrointestinal bleeding (at least two distinct episodes of proven ulceration or bleeding)
- if your child has ever had bleeding or perforation in the stomach or intestines when taking NSAIDs.
- if you have a cerebral hemorrhage or other active bleeding.
- if your child has severe liver or kidney problems or severe heart problems that are not adequately treated.
- if your child has severe heart failure (heart failure).
- severe dehydration (due to vomiting, diarrhea or not drinking enough fluids).
- during the last three months of pregnancy.
pregnancy and breast feeding period
- If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking/using this medicine.
- pregnancy
- If pregnancy is detected while using ibuprofen, the doctor must be notified. You may only take the preparation in the first 6 months of pregnancy after consulting your doctor. Because of an increased risk of complications for mother and child, the drug must not be taken in the last 3 months of pregnancy.
- lactation
- Only small amounts of the active ingredient ibuprofen and its breakdown products pass into breast milk. Since there are no known adverse effects on the infant, discontinuation of breastfeeding is generally not necessary with short-term use of the dose recommended for the treatment of mild to moderate pain or fever.
patient notes
- Warnings and Precautions.
- Please talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using the medicine in the following cases.
- in congenital blood formation disorders (e.g. acute intermittent porphyria).
- in certain diseases of the immune system (systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed collagenosis).
- if you have impaired kidney or liver function.
- if your child suffers from dehydration (e.g. vomiting or diarrhoea).
- if you have high blood pressure or heart failure (heart failure).
- if your child suffers from allergies (e.g. skin reactions to other medicines, asthma, hay fever), nasal polyps, chronic swelling of the nasal mucosa or chronic airway diseases that narrow the airways - their risk of hypersensitivity reactions is then increased.
- shortly after major surgery.
- Side effects can be reduced by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest amount of time needed to control symptoms.
- Ibuprofen belongs to a group of medicines (NSAIDs) that can affect fertility in women. This effect is reversible (reversible) after stopping the drug.
- Gastrointestinal safety
- The concomitant use of ibuprofen with other medicinal products from the group of NSAIDs, including selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, should be avoided.
- Elderly people:
- Older people are more likely to experience side effects when using NSAIDs, particularly bleeding or perforation in the stomach and intestines, which can be fatal.
- Bleeding, ulcer and perforation in the gastrointestinal tract:
- Bleeding, ulceration and perforation of the stomach or intestines, including fatal outcomes, have been reported during treatment with all NSAIDs. They occurred with or without prior warning symptoms or a history of serious gastrointestinal events at any time during therapy.
- The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration or perforation is higher with increasing NSAID doses, in patients with a history of ulcer, particularly if complicated with bleeding or perforation, and in the elderly. In this case you should start treatment with the lowest available dose. Please talk to your doctor about whether a combination treatment with a medicine that protects the stomach lining (e.g. misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors) makes sense for you. This also applies if you are also taking low doses of acetylsalicylic acid or other medicines that can increase the risk of side effects in the gastrointestinal tract.
- If you have ever had a drug that has caused side effects in the gastrointestinal tract, you should - especially if you are elderly - have any unusual
abdominal symptoms (especially bleeding in the gastrointestinal area), especially at the beginning of the treatment, speak to your doctor immediately. Caution is advised if you are also taking medicines that may increase the risk of gastrointestinal ulcers or bleeding, e.g. B.
oral cortisone preparations, anticoagulants (blood-thinning) agents such as warfarin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or platelet aggregation inhibitors such as acetylsalicylic acid. - If bleeding or ulcers in the gastrointestinal tract occur during treatment with the medicine, the treatment must be stopped and a doctor consulted.
- NSAIDs should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease) as their condition
may worsen (see category "Side effects")
- Effects on the blood vessels of the heart and brain (cardiovascular and cerebrovascular effects)
- Anti-inflammatories/painkillers such as ibuprofen may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack or stroke, particularly when used in high
doses. Do not exceed the recommended dose or duration of treatment (3 days). - You should discuss your treatment with your doctor or pharmacist before taking ibuprofen if you:
- have heart disease, including heart failure (heart failure) and angina (chest pain), or have had a heart attack, bypass surgery, peripheral artery disease (poor circulation in the legs or feet due to narrow or blocked arteries), or any type of stroke (including mini had a stroke or transient ischemic attack ("TIA").
- have high blood pressure, diabetes or high cholesterol, or a family history of heart disease or stroke, or if you are a smoker.
- Anti-inflammatories/painkillers such as ibuprofen may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack or stroke, particularly when used in high
- skin reactions
- Serious skin reactions have been reported in association with treatment with ibuprofen. If you develop a skin rash, lesions on the mucous membranes, blisters or
other signs of allergy, you should stop taking the medicine and seek medical attention immediately, as these can be the first signs of a very serious skin reaction (see category "Side effects"). - During a chickenpox infection, it is advisable to avoid the use of the preparation.
- Serious skin reactions have been reported in association with treatment with ibuprofen. If you develop a skin rash, lesions on the mucous membranes, blisters or
- Further information
- Severe acute hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. anaphylactic shock) have been observed very rarely after taking ibuprofen. Treatment must be
stopped immediately at the first sign of a hypersensitivity reaction after ingestion/application of ibuprofen. The necessary medical measures depend on the symptoms that have occurred and must be initiated by medical professionals. - Your child should drink enough fluids during treatment, especially if they have fever, diarrhea or vomiting. There is a risk of renal dysfunction in dehydrated children.
- Ibuprofen, the active ingredient in the preparation, can temporarily inhibit the function of the blood platelets (platelet aggregation). Patients with bleeding disorders should therefore be carefully
monitored. - With prolonged use of ibuprofen, regular monitoring of liver enzymes, kidney function and blood count is required.
- Long-term use of painkillers can cause headaches that should not be treated with higher doses of the drug.
- In general, the habitual intake of painkillers, especially when several painkillers are combined, can lead to permanent kidney damage with the risk of kidney failure (so-called analgesic nephropathy).
- Severe acute hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. anaphylactic shock) have been observed very rarely after taking ibuprofen. Treatment must be
- Please talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using the medicine in the following cases.
- Driving and using machines
- Since side effects such as tiredness, dizziness and visual disturbances can occur during treatment with ibuprofen, the ability to react and the ability to drive and use machines may be impaired in individual cases. This applies to a greater extent in combination with alcohol.
- Manufacturer: ratiopharm GmbH